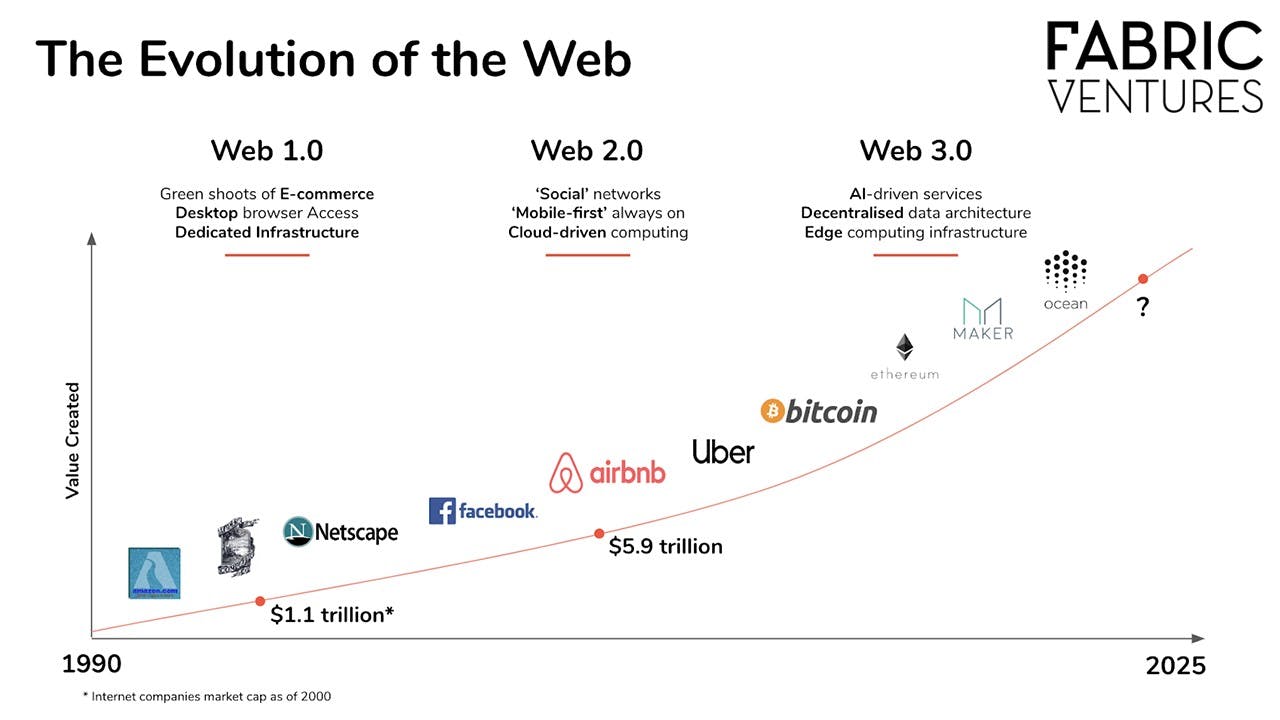
It makes sense to understand Web 3 by first understanding what goes before it. Web 1, the first online version, was released in the late 1990s and included a collection of links and home pages. The websites were not very interactive. Apart from reading and publishing basic content for others to read, there is not much you can do.
In a speech to the Congress of the United States in December 2021, Brian Brooks, CEO of Bitfury, summed it up: "When people remember their first AOL account, it was the ability to view 'walled garden' content that was not uncommon, but presented to you in -AOL, the way Time Magazine used it to show you the articles they wanted to see inside their magazine, only you can see it on screen."
Web 2 followed. Some refer to this as the "read/write" internet, referring to a computer code that allows you to open and edit files rather than just view them. This version of the Internet allowed people to create their own content and publish it on blogs like Tumblr, Internet forums, and marketplaces like Craigslist. Later, with the rise of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, content sharing reached new heights.
After a while, the general public became aware of how tech giants were harvesting their personal data and using it to create tailored advertisements and marketing campaigns. Facebook, in particular, has been scrutinized numerous times for violating data privacy laws and was fined $5 billion in 2019 – the largest penalty ever imposed by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC.)
Although Web 2 offers amazing free services around the world, many people are tired of the new "walled gardens" created by these big technology companies and want more control over their data and content. This is where Web 3 comes into play.
Web 3 can be thought of as an online "read / write / write / write" section. Users can participate in the governance and implementation of agreements rather than simply accessing our data through free technology forums. This means that people can become shareholders rather than just customers.
Blockchains are tokens or cryptocurrencies used on Web 3 to represent the ownership of isolated networks. If you own enough of these tokens, you can exert influence on the network. Owners of administrative tokens, for example, can use their funds to vote on the future of a decentralized loan protocol.
The real takeaway here is that what happens on a diverse internet is determined by investors, whereas what happens on the big internet is determined by Twitter, Facebook, Google, and a few other companies.
Now that it is clear to you so let’s see the advantages and Disadvantages of Web3.
As data infrastructure improves people are increasingly demanding that data be accessible and retain control of their information. The default Blockchain data system allows data to be stored in such a way that it remains under the control of the owner, even if it is stored on a business server or under local government control.
Owners or governing bodies will not be able to access or edit data unless they have encryption keys that prove they are the rightful owners. Additionally, even if they shut down or delete their server, the data will still be accessible to one of the hundreds of other devices where it is stored.
With the launch of Web3.0, progress in the online world continues. Web3.0 is the third generation of the Internet, and it is growing rapidly.
Here are some of the advantages of Web3.0:
- Improvements to the appearance of the semantic web
- More efficient web browsing
- Persuasive correspondence
- Communication transformation
- Search results that are more credible and valid
- Working on the internet will become much easier as it becomes personalized.
- Knowledge exchange is more accessible.
Here are some of the potential barriers to Web3.0:
- Web3.0 will not be accessible to less advanced devices.
- Web1.0 websites will appear more frequently than ever before.
- Web3.0 is very difficult for newcomers to understand
- The technology is not really ready yet
- It is difficult to use
- People will spend a lot of time online
- Privacy rules will be needed to protect them.
How Web3 can be used in the Fintech Industry and how it has already Impacted the Industry?
The evolution of FinTech globally changed dramatically over time, becoming a roaring opportunity on Wall Street and Silicon Valley. FinTech's growing power from 1.0 to 3.0 has forced traditional banking systems and financial services providers to embark on a transition that will usher in a new era of the digital world. The remarkable transformation of the World Wide Web started with Web 3.0, which is backed by technologies such as machine-learning architecture and reshapes the financial services business with a more general, segmented work model.
The maturing Web 3.0 ecosystem, led by decentralized autonomous organizations, has fueled global demand for structured financial products enabled by superfast 5G data speeds, data formats, and software.
So, in this modern global economy, we'll take a deep dive into understanding the mutual relationship between Web 3.0 and the FinTech industry.
The first two waves further the momentum of FinTech 3.0, increasing the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to flourish intelligent and independent processes. Many world powers are involved in developing and advancing a new wave of innovation, with the emergence of the Web playing an important role.
Web 1.0, the first phase of World Wide Web evolution, empowers users to share consistent information around the world by making democracy accessible to information. After the dot-com bubble, Web 2.0 transformed the digital age by emphasizing social media, user-generated content, and cloud computing, creating social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and many more.
Finally, Web 3.0, also known as the decentralized web, is a vision of the internet's future in which computers and technologies deliver useful and relevant insights through intelligent data and transaction interpretation. FinTech 3.0's new cashless and virtual economy necessitates Web 3.0 transformation to lay the groundwork for how businesses deliver products and services to next-generation unicorns.
Now let’s see how web3 will benefit the Fintech Industry with some of the departments.
By disrupting the way individuals, businesses, and regulatory organizations collaborate and plan to collaborate, the third generation of internet services will enable a more connected and intelligent world for the financial services industry. Here are the top advantages of our new decentralized operating model and Web 3.0 convergence:
1. TRUSTWORTHINESS Web 3.0 will make the onboarding process simpler and more user-friendly. Web 3.0 will ensure that end-users always have complete ownership and control over their online data by utilizing decentralized networks. Every subsequent evolution of the Web will ensure even greater trustworthiness for businesses by removing security concerns about storing any data.
2. IMPROVED CUSTOMER JOURNEY Web 3.0 will help FinTech companies better understand the changing needs of their customers and their expectations. Businesses can automate customer visit mapping processes and allocate resources more efficiently with the Web 3.0 list of technology offerings to meet customer needs, facilitate better collaboration, and promote long-term reliability.
3. UNINTERRUPTED SERVICE Because data will be stored in distributed locations due to fragmentation, Web 3.0 will significantly reduce account suspension and denial of distributed services. This will also help FinTech companies reduce hosting costs or server failures.
So we can finally say that the current rate of maturation of the FinTech industry has created an enormous demand for digital lending technology partners across businesses worldwide. Next-generation businesses are looking for a trusted partner who understands the current state of the FinTech market driven by Web 3.0 to unleash innovation to scale quickly. Partnerships like these provide an excellent opportunity to differentiate your company in this highly competitive world!
How realistic for the finance industry, specifically banks and fintech’s moving to web3 and DeFi.
What we can say right now is that banks really don’t like getting into Defi and Web3 or you can say into anything related to Cryptocurrencies. But obviously, the reasons differ by jurisdiction and bank; after all, the world is a huge place.
However, lawyers and banking professionals explain why some banks refuse to process crypto transactions and offer advice on what to do if your bank refuses to process a relevant transaction.
Many countries do not recognize cryptocurrencies, making it unlawful for banks to handle Bitcoin-related transactions. Banks in China and Bolivia, for example, will not execute Bitcoin transactions since it is illegal.
Even in areas where cryptocurrency is legal, some banks don't want to deal with irate clients asking for chargebacks from a crypto-related Ponzi scheme because they don't believe it's worth the effort. Some customers may not be aware of all the risks associated with cryptocurrency and banks don't want to pay for consumers who aren't well-informed—cheaper it's to avoid crypto entirely.
Banks do not want the difficulty of dealing with cryptocurrency-related crimes, whether their customers are perpetrators or victims. For many banks, the costs of dealing with their customers' cryptocurrency issues, as well as setting up cryptocurrency fraud or fraud prevention programs, are not worth the effort to work for what is still a small sector.
###But these were the reasons for which Bank doesn’t want to go for adopting Defi and Web3 but now let’s discuss why they should get into Defi and Web3. As recently, traditional banks made a mistake. Due to their precarious position and conservatism, the world's largest financial institutions have missed out on the rapid development of FinTech. Banks were forced to develop new solutions after the fact and quickly, which cost small FinTech firms market share. And now banks risk making the same mistake again, this time about Defi and Web3.
While cautious banks wait and watch, limiting bitcoin's future, companies like SEBA and Wirex are constructing a comprehensive ecosystem that combines fiat and Defi. These companies were among the first to connect the old financial system to the blockchain, and others should follow in their footsteps to avoid making the same mistake.
No amount of market growth or aggressive attempts by financial authorities to develop a common framework has been able to persuade banks of the legitimacy of the cryptocurrency and Defi industry. Extreme currency fluctuations and a lack of banking infrastructure in the emerging economy drive the growth of Decentralized Finance.
Defi has gained a lot in Mexico, India, and many African countries. The young people of these nations are eagerly learning new technologies, and Crypto trading is fast becoming the easiest way for them to send money. Banks considering expanding to emerging regions should keep in mind that Defi and Web 3 already have a place in the market.
So let’s finally find out that can we declare Web 3 the future of Finance?
As mentioned above in the article that the internet has undergone significant disruptions, transitioning from offering read-only, static content at its inception to a much more dynamic, interactive, and decentralized experience today. Web 3.0 is evolving as a result of innovations in decentralized finance (DeFi), blockchain, cryptocurrencies, and distributed ledgers. The total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies was $2.2 trillion in December 2021, while the total locked value in DeFi protocols increased by over 1000 percent year on year.
We can easily say that Web3 will be the future of Finance. You may have heard or seen that Elon Musk has bought Twitter and Binance’s CEO is also involved in it so they are maybe planning to adopt crypto for Twitter which will obviously open the ways of Web 3 and Defi in General And due to the launch of Crypto.Com’s CRO card and Binance’s Binance card for payments things are already not good for Banks and Financial sectors so let’s see what happens next.

